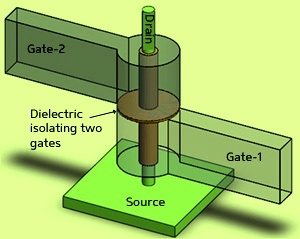
Electronics, embedded, microcontroller, pic, projects, hobby circuits, circuit, blog, transistor, technology
What’s Inside an Electrolytic Capacitor?
The aluminium electrolytic capacitor consists of two foils sandwiched between absorbent paper, and wound tightly into a cylinder. The anode, is composed of pure aluminium foil with aluminium oxide formed electrolytically on the surface. The foil has been etched to increase the effective surface area. The cathode is made of high-absorption paper mixed with an electrolyte, in contact with a cathode foil. The electrolyte is used to ensure good contact with the anode, by permeating its etched structure, and also to repair any flaws in the oxide layer when the capacitor is polarised....